Autonomous Vehicles: The Road to a Driverless Future
The concept of autonomous vehicles (AVs) has long captured the imagination of technologists, car enthusiasts, and futurists alike. In many ways, these vehicles represent the next frontier in transportation, promising to reshape how we navigate our cities, improve road safety, and offer new levels of convenience and efficiency. While fully autonomous vehicles have yet to become a mainstream reality, the progress made in recent years suggests that a driverless future is within reach. This article explores the journey of autonomous vehicles, the technology behind them, and the challenges and opportunities they present for society.
What Are Autonomous Vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars or driverless cars, are vehicles capable of sensing their environment and operating without human intervention. Through a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI), AVs can navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make decisions based on real-time data, all while adhering to traffic laws and regulations.
The level of autonomy varies in these vehicles, ranging from partially autonomous systems, where the driver still has control of the vehicle but can delegate some tasks (like adaptive cruise control), to fully autonomous vehicles (Level 5) that require no human interaction at all.
The Technology Behind Autonomous Vehicles
The development of autonomous vehicles relies on cutting-edge technology, particularly in the fields of AI, machine learning, and sensor integration. Key components of autonomous vehicles include:
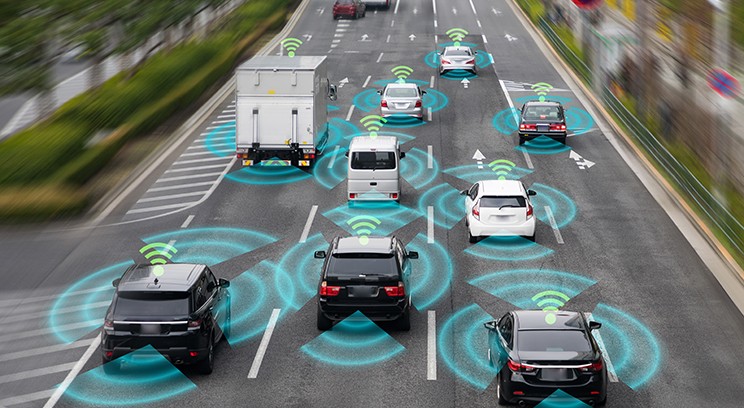
- Sensors and Cameras: Autonomous vehicles are equipped with various sensors, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and ultrasonic sensors. These technologies work together to create a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings. LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure distances and create high-resolution maps of the environment, while radar detects objects and measures their speed. Cameras are used to capture visual data for object recognition, lane detection, and traffic signal identification.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The heart of an autonomous vehicle’s decision-making process lies in artificial intelligence. AVs use machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data from the sensors and cameras, enabling them to “learn” from their environment. By analyzing patterns, the vehicle can predict and react to situations, such as avoiding obstacles or adjusting speed for traffic conditions.
- Mapping and Navigation: Autonomous vehicles rely on detailed maps that include not only roads but also information such as traffic patterns, road signs, and other variables that might impact navigation. These maps are continuously updated using real-time data from both the vehicle and infrastructure (e.g., smart traffic lights or road sensors) to ensure safe and efficient travel.
- Connectivity: Autonomous vehicles are often equipped with vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication systems. This connectivity enables vehicles to share information with each other and with surrounding infrastructure, improving safety by providing real-time updates on traffic conditions, accidents, or road hazards.
The Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
- Enhanced Road Safety One of the most compelling reasons for the development of autonomous vehicles is the potential to significantly reduce traffic accidents. Human error is responsible for approximately 94% of all traffic crashes, and AVs have the potential to eliminate these mistakes. Through precise, data-driven decision-making and faster reaction times, autonomous vehicles can reduce accidents caused by factors like distracted driving, fatigue, or impaired driving.
- Increased Mobility and Accessibility Autonomous vehicles have the potential to improve mobility for individuals who are unable to drive, including the elderly and disabled. These vehicles can provide a level of independence for people who rely on public transportation or the assistance of others for mobility. In addition, AVs could increase overall accessibility to transportation, making it easier for people to access work, education, and healthcare services.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion By utilizing advanced communication systems and optimizing driving patterns, autonomous vehicles could help reduce traffic congestion. AVs can communicate with each other to maintain optimal speed and spacing, leading to smoother traffic flow. In addition, the ability to adapt to real-time traffic conditions could minimize delays and improve efficiency, particularly in urban areas.
- Environmental Benefits Many autonomous vehicles are designed with energy efficiency in mind. As the majority of AVs on the road are electric, their widespread adoption could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Moreover, the ability of AVs to optimize routes and reduce idle time could lead to significant improvements in fuel efficiency.
- Cost Savings Over time, the adoption of autonomous vehicles could lead to significant cost savings. AVs could reduce the need for parking, as they can drop passengers off at their destination and continue to park themselves in remote locations or on-demand spaces. Additionally, by improving traffic flow and reducing accidents, autonomous vehicles could help lower insurance premiums and healthcare costs related to traffic injuries.
Challenges in Achieving a Fully Autonomous Future
While the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are vast, there are still several significant challenges to overcome before fully driverless cars become commonplace:
- Regulatory and Legal Issues The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles will require a comprehensive legal framework to ensure safety, liability, and insurance standards are met. Governments must address questions around who is responsible for accidents involving autonomous vehicles (manufacturers, software developers, or vehicle owners). Additionally, regulatory agencies will need to develop new traffic laws and road safety guidelines that account for the unique capabilities and limitations of AVs.
- Public Trust and Acceptance Public trust in autonomous vehicles remains a significant hurdle. Many individuals are still skeptical about the safety and reliability of AVs, especially following incidents involving self-driving cars. Building consumer confidence will require extensive testing, transparency, and clear communication about how AV technology works to mitigate risks and improve safety.
- Technology and Infrastructure Limitations While autonomous vehicles are advancing rapidly, they still face limitations in terms of technology. For example, AVs may struggle in challenging conditions, such as extreme weather (snow, fog, heavy rain) or complex urban environments with unmarked roads or poor infrastructure. Furthermore, the widespread deployment of autonomous vehicles requires significant upgrades to existing infrastructure, such as smart traffic signals and enhanced road sensors, to ensure seamless integration and safety.
- Cybersecurity Risks As autonomous vehicles rely heavily on digital systems and connectivity, they are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. Hackers could potentially gain control of AVs, leading to serious safety risks. To address these concerns, robust cybersecurity measures must be put in place to protect the vehicles from malicious attacks and unauthorized access.
- Job Displacement The introduction of autonomous vehicles could lead to job displacement in sectors like transportation, logistics, and delivery. Truck drivers, taxi drivers, and chauffeurs may face unemployment as AVs become more widespread. While new jobs will be created in tech, maintenance, and infrastructure, addressing the economic impact of this shift will require strategic planning and retraining programs.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
The future of autonomous vehicles is undoubtedly exciting, but it is still evolving. Major automakers and tech companies are investing heavily in AV research, and recent advancements in AI and machine learning are accelerating the development process. Over the next few decades, we may see a gradual transition from human-driven to self-driving vehicles on our roads, beginning with partial autonomy and progressing to full autonomy.
It is likely that autonomous vehicles will initially coexist with traditional vehicles, especially in the early stages of adoption. However, as technology improves and infrastructure becomes more supportive, fully driverless cars could eventually become the norm, reshaping the landscape of personal and commercial transportation.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles are on the cusp of revolutionizing the transportation industry. The road to a driverless future is not without its challenges, but the potential benefits are undeniable. From increased safety and mobility to reduced traffic congestion and environmental impact, autonomous vehicles offer an exciting glimpse into a more efficient and accessible future. As technology, regulation, and public perception continue to evolve, autonomous vehicles are poised to become a cornerstone of the next generation of transportation, bringing us closer to a world where the car drives itself